Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is a bacterium that naturally resides in the intestines of humans and animals. While many strains are harmless and play a role in maintaining a healthy gut, certain variants can lead to severe illness. Recent events have highlighted the importance of understanding the causes of E. coli infections and the measures necessary to prevent them.
Causes of E. coli Infections
E. coli infections primarily result from ingesting contaminated food or water. The bacterium can be transmitted through various means:
- Contaminated Food: Undercooked ground beef is a common source of E. coli. The grinding process can distribute bacteria throughout the meat, making thorough cooking essential. Additionally, raw milk and dairy products made from unpasteurized milk can harbor harmful E. coli strains. Fresh produce, such as lettuce and spinach, can become contaminated through contact with animal feces during cultivation or handling.
- Contaminated Water: Drinking or swimming in water contaminated with E. coli can lead to infection. This contamination often occurs when water sources are exposed to sewage or agricultural runoff.
- Person-to-Person Contact: E. coli can spread from an infected individual to others, especially if proper hygiene practices are not followed. This is particularly concerning in settings like daycare centers or nursing homes, where individuals may have weakened immune systems.
- Animal Contact: Direct interaction with animals, especially in petting zoos or farms, can expose individuals to E. coli present in animal feces.
Recent Outbreaks and Public Health Concerns
In recent months, there have been notable E. coli outbreaks linked to popular food establishments. A significant incident involved McDonald’s Quarter Pounder burgers, which were associated with a multi-state E. coli outbreak. Investigations suggested that slivered onions used in these burgers were the probable source of contamination. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported 49 illnesses across 10 states, with 10 hospitalizations and one fatality. In response, McDonald’s ceased using the implicated onions and suspended the sale of Quarter Pounders in affected areas.
These events underscore the critical importance of stringent food safety protocols and the need for consumers to remain vigilant about the sources of their food.
Preventive Measures
Preventing E. coli infections involves a combination of proper food handling, personal hygiene, and awareness:
- Food Handling:
- Cook Meat Thoroughly: Ensure ground beef and other meats are cooked to safe internal temperatures to kill any present bacteria.
- Avoid Raw Milk: Consume only pasteurized dairy products to reduce the risk of infection.
- Wash Produce: Rinse fruits and vegetables under running water before consumption, even if they will be peeled.
- Personal Hygiene:
- Hand Washing: Regularly wash hands with soap and water, especially after using the restroom, handling raw meat, or interacting with animals.
- Sanitize Surfaces: Clean kitchen surfaces, utensils, and cutting boards after contact with raw meat to prevent cross-contamination.
- Water Safety:
- Drink Safe Water: Consume water from reliable sources. If the safety of water is questionable, boil it before drinking.
- Recreational Water: Avoid swallowing water from pools, lakes, or rivers, and ensure public swimming areas are properly maintained.
The Human Impact
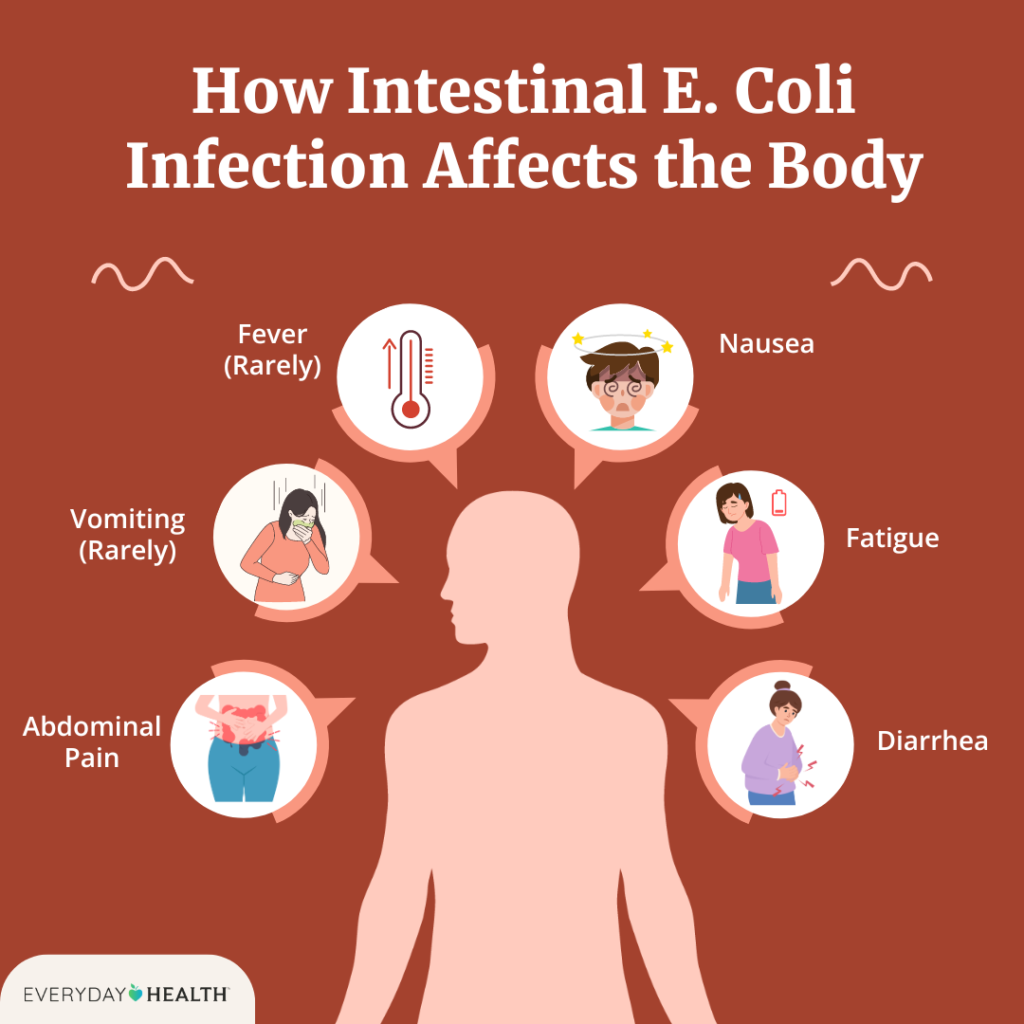
Beyond the clinical aspects, E. coli infections can have profound effects on individuals and communities. Symptoms such as severe stomach cramps, diarrhea (often bloody), and vomiting can lead to significant discomfort and, in severe cases, life-threatening complications like hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), which affects the kidneys.
The psychological impact of outbreaks, especially those linked to popular food establishments, can erode public trust in food safety systems. Families affected by severe cases may experience emotional and financial strain due to medical treatments and prolonged recovery periods.
Understanding the causes of E. coli infections is essential for prevention and maintaining public health. Recent outbreaks serve as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities in our food supply chain and the importance of rigorous safety measures. By adhering to recommended preventive practices and staying informed about potential risks, individuals can protect themselves and contribute to broader community health efforts.
