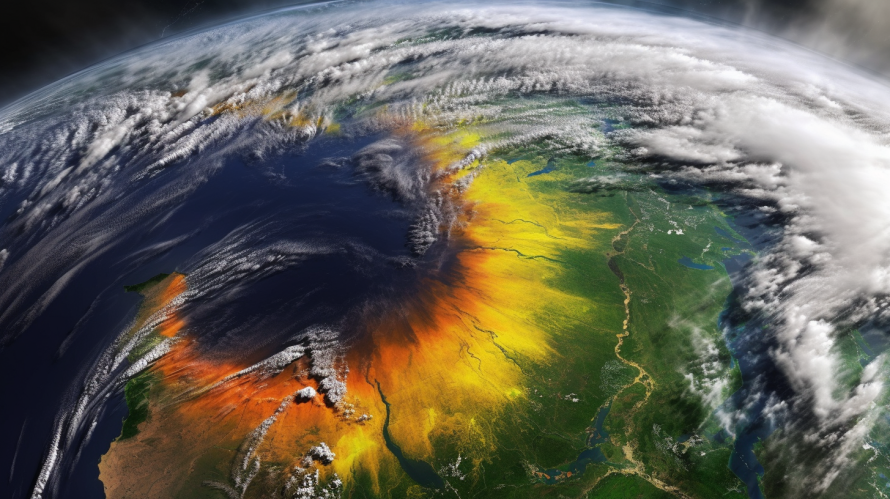
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis was one of the most destructive storms to hit Japan in recent years. The storm caused widespread damage and flooding across several regions, leading to significant economic losses. In this article, we will explore how did Tropical Cyclone Hagibis impact the economy, including its effects on businesses, infrastructure, and tourism.
Background
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis struck Japan in October 2019, causing extensive damage and flooding across several regions. The storm made landfall in the Izu Peninsula on October 12, before moving northward and causing flooding and landslides in Tokyo and other regions. The storm resulted in over 90 deaths, with hundreds more injured or missing.
Impact on Infrastructure
One of the most significant impacts of Tropical Cyclone Hagibis was on infrastructure. The storm caused widespread flooding and landslides, leading to the closure of roads, railways, and airports. The flooding and landslides also damaged bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure, leading to significant repair costs. The storm caused estimated damages of over $10 billion, making it one of the costliest disasters in Japan’s history.
Impact on Businesses
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis also had a significant impact on businesses, particularly those in the retail and hospitality industries. The storm hit during a busy holiday period, causing many shops, restaurants, and tourist attractions to close. The closures and reduced foot traffic resulted in significant losses for businesses, particularly those in the tourism industry. The storm also disrupted supply chains, leading to shortages of goods and increased costs for businesses.
Impact on Agriculture
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis also had a significant impact on Japan’s agricultural sector. The storm caused extensive flooding and landslides in rural areas, damaging crops and infrastructure. The damage led to a decline in agricultural output and a reduction in exports, leading to economic losses for farmers and the wider agricultural industry.
Impact on Tourism
Tourism is a significant contributor to the Japanese economy, and Tropical Cyclone Hagibis had a significant impact on the industry. The storm hit during a busy holiday period, leading to the cancellation of many flights and hotel bookings. The closures of tourist attractions, including theme parks and museums, also led to a decline in tourist numbers. The impact of the storm on tourism is estimated to have caused economic losses of over $1 billion.
Government Response
The Japanese government responded to Tropical Cyclone Hagibis with a range of measures aimed at mitigating the economic impact of the storm. These measures included financial assistance for affected businesses and individuals, as well as funding for repair and rebuilding efforts. The government also implemented measures to support the agricultural sector, including subsidies for farmers and assistance with crop replanting. The government’s response was generally well-received, although some criticized the speed and effectiveness of the measures.
Lessons Learned
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis highlighted the need for better disaster preparedness and response in Japan. The storm exposed weaknesses in the country’s infrastructure and emergency response systems, leading to calls for improvements in these areas. The storm also highlighted the need for businesses to have disaster preparedness plans in place, particularly those in the tourism industry.
Conclusion
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis had a significant impact on the Japanese economy, causing extensive damage and flooding across several regions. The storm resulted in economic losses of over $10 billion, with significant impacts on businesses, infrastructure, and tourism. The government’s response to the storm was generally well-received, although there were criticisms of the speed and effectiveness of the measures. The storm highlighted the need for better disaster preparedness and response in Japan, as well as the need for businesses to have disaster preparedness plans in place.